首页 > Python基础教程 >
-
C#中HttpWebRequest、WebClient、HttpClient的使用详解
HttpWebRequest:
命名空间: System.Net,这是.NET创建者最初开发用于使用HTTP请求的标准类。使用HttpWebRequest可以让开发者控制请求/响应流程的各个方面,如 timeouts, cookies, headers, protocols。另一个好处是HttpWebRequest类不会阻塞UI线程。例如,当您从响应很慢的API服务器下载大文件时,您的应用程序的UI不会停止响应。HttpWebRequest通常和WebResponse一起使用,一个发送请求,一个获取数据。HttpWebRquest更为底层一些,能够对整个访问过程有个直观的认识,但同时也更加复杂一些。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
//POST方法public static string HttpPost(string Url, string postDataStr){ HttpWebRequest request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(Url); request.Method = "POST"; request.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded"; Encoding encoding = Encoding.UTF8; byte[] postData = encoding.GetBytes(postDataStr); request.ContentLength = postData.Length; Stream myRequestStream = request.GetRequestStream(); myRequestStream.Write(postData, 0, postData.Length); myRequestStream.Close(); HttpWebResponse response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse(); Stream myResponseStream = response.GetResponseStream(); StreamReader myStreamReader = new StreamReader(myResponseStream, encoding); string retString = myStreamReader.ReadToEnd(); myStreamReader.Close(); myResponseStream.Close(); return retString;}//GET方法public static string HttpGet(string Url, string postDataStr){ HttpWebRequest request = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(Url + (postDataStr == "" ? "" : "?") + postDataStr); request.Method = "GET"; request.ContentType = "text/html;charset=UTF-8"; HttpWebResponse response = (HttpWebResponse)request.GetResponse(); Stream myResponseStream = response.GetResponseStream(); StreamReader myStreamReader = new StreamReader(myResponseStream, Encoding.GetEncoding("utf-8")); string retString = myStreamReader.ReadToEnd(); myStreamReader.Close(); myResponseStream.Close(); return retString;} |
WebClient:
命名空间System.Net,WebClient是一种更高级别的抽象,是HttpWebRequest为了简化最常见任务而创建的,使用过程中你会发现他缺少基本的header,timeoust的设置,不过这些可以通过继承httpwebrequest来实现。相对来说,WebClient比WebRequest更加简单,它相当于封装了request和response方法,不过需要说明的是,Webclient和WebRequest继承的是不同类,两者在继承上没有任何关系。使用WebClient可能比HttpWebRequest直接使用更慢(大约几毫秒),但却更为简单,减少了很多细节,代码量也比较少。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
|
public class WebClientHelper { public static string DownloadString(string url) { WebClient wc = new WebClient(); //wc.BaseAddress = url; //设置根目录 wc.Encoding = Encoding.UTF8; //设置按照何种编码访问,如果不加此行,获取到的字符串中文将是乱码 string str = wc.DownloadString(url); return str; } public static string DownloadStreamString(string url) { WebClient wc = new WebClient(); wc.Headers.Add("User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/76.0.3809.132 Safari/537.36"); Stream objStream = wc.OpenRead(url); StreamReader _read = new StreamReader(objStream, Encoding.UTF8); //新建一个读取流,用指定的编码读取,此处是utf-8 string str = _read.ReadToEnd(); objStream.Close(); _read.Close(); return str; } public static void DownloadFile(string url, string filename) { WebClient wc = new WebClient(); wc.DownloadFile(url, filename); //下载文件 } public static void DownloadData(string url, string filename) { WebClient wc = new WebClient(); byte [] bytes = wc.DownloadData(url); //下载到字节数组 FileStream fs = new FileStream(filename, FileMode.Create); fs.Write(bytes, 0, bytes.Length); fs.Flush(); fs.Close(); } public static void DownloadFileAsync(string url, string filename) { WebClient wc = new WebClient(); wc.DownloadFileCompleted += DownCompletedEventHandler; wc.DownloadFileAsync(new Uri(url), filename); Console.WriteLine("下载中。。。"); } private static void DownCompletedEventHandler(object sender, AsyncCompletedEventArgs e) { Console.WriteLine(sender.ToString()); //触发事件的对象 Console.WriteLine(e.UserState); Console.WriteLine(e.Cancelled); Console.WriteLine("异步下载完成!"); } public static void DownloadFileAsync2(string url, string filename) { WebClient wc = new WebClient(); wc.DownloadFileCompleted += (sender, e) => { Console.WriteLine("下载完成!"); Console.WriteLine(sender.ToString()); Console.WriteLine(e.UserState); Console.WriteLine(e.Cancelled); }; wc.DownloadFileAsync(new Uri(url), filename); Console.WriteLine("下载中。。。"); } } |
HttpClient:
HttpClient是.NET4.5引入的一个HTTP客户端库,其命名空间为 System.Net.Http ,.NET 4.5之前我们可能使用WebClient和HttpWebRequest来达到相同目的。HttpClient利用了最新的面向任务模式,使得处理异步请求非常容易。它适合用于多次请求操作,一般设置好默认头部后,可以进行重复多次的请求,基本上用一个实例可以提交任何的HTTP请求。HttpClient有预热机制,第一次进行访问时比较慢,所以不应该用到HttpClient就new一个出来,应该使用单例或其他方式获取HttpClient的实例
单例模式:
单例模式(Singleton Pattern)这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式。
这种模式涉及到一个单一的类,该类负责创建自己的对象,同时确保只有单个对象被创建。这个类提供了一种访问其唯一的对象的方式,可以直接访问,不需要实例化该类的对象。
单例创建步骤:1、定义静态私有对象;2、定义私有构造函数;3、提供公共获取对象方法;
单例模式一般分为两种实现模式:懒汉模式、饿汉模式(以下为Java代码实现)
懒汉模式: 默认不会实例化,什么时候用什么时候new
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public class Singleton { private static Singleton instance = null; private Singleton (){} public static Singleton getInstance() { if (instance == null) { instance = new Singleton(); } return instance; } } |
这种方式是最基本的实现方式,这种实现最大的问题就是不支持多线程。因为没有加锁 synchronized,所以严格意义上它并不算单例模式。
这种方式 lazy loading 很明显,不要求线程安全,在多线程不能正常工作。
饿汉模式: 类初始化时,会立即加载该对象,线程天生安全,调用效率高
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public class Singleton { private static Singleton instance = new Singleton(); private Singleton (){} public static Singleton getInstance() { return instance; } } |
双检锁/双重校验锁(DCL,即 double-checked locking):这种方式采用双锁机制,安全且在多线程情况下能保持高性能
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public class Singleton { private volatile static Singleton singleton; private Singleton (){} public static Singleton getSingleton() { if (singleton == null) { synchronized (Singleton.class) { if (singleton == null) { singleton = new Singleton(); } } } return singleton; } } |
HttpClient:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
|
public class HttpClientHelper { private static readonly object LockObj = new object(); private static HttpClient client = null; public HttpClientHelper() { GetInstance(); } public static HttpClient GetInstance() { if (client == null) { lock (LockObj) { if (client == null) { client = new HttpClient(); } } } return client; } public async Task<string> PostAsync(string url, string strJson)//post异步请求方法 { try { HttpContent content = new StringContent(strJson); content.Headers.ContentType = new System.Net.Http.Headers.MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/json"); //由HttpClient发出异步Post请求 HttpResponseMessage res = await client.PostAsync(url, content); if (res.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK) { string str = res.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result; return str; } else return null; } catch (Exception ex) { return null; } } public string Post(string url, string strJson)//post同步请求方法 { try { HttpContent content = new StringContent(strJson); content.Headers.ContentType = new System.Net.Http.Headers.MediaTypeHeaderValue("application/json"); //client.DefaultRequestHeaders.Connection.Add("keep-alive"); //由HttpClient发出Post请求 Task<HttpResponseMessage> res = client.PostAsync(url, content); if (res.Result.StatusCode == System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK) { string str = res.Result.Content.ReadAsStringAsync().Result; return str; } else return null; } catch (Exception ex) { return null; } } public string Get(string url) { try { var responseString = client.GetStringAsync(url); return responseString.Result; } catch (Exception ex) { return null; } } } |
HttpClient有预热机制,第一次请求比较慢;可以通过初始化前发送一次head请求解决:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
_httpClient = new HttpClient() { BaseAddress = new Uri(BASE_ADDRESS) }; //帮HttpClient热身 _httpClient.SendAsync(new HttpRequestMessage { Method = new HttpMethod("HEAD"), RequestUri = new Uri(BASE_ADDRESS + "/") }) .Result.EnsureSuccessStatusCode(); |
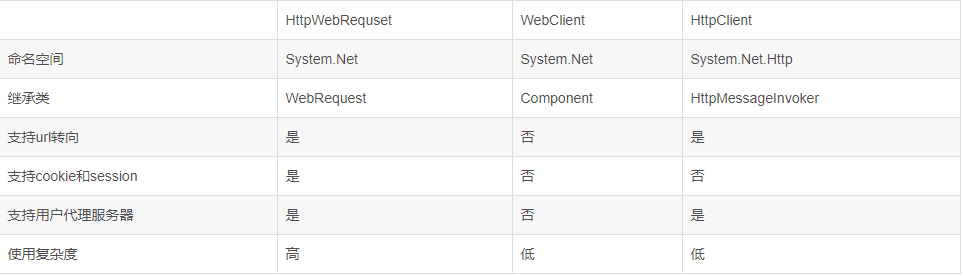
三者区别列表:
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持脚本之家。










